Department of Computer Science
We are an internationally-oriented community and home to world-class research in modern computer science.

With over four billion people eligible to vote in elections, 2024 is the largest election year ever. At the same time, disinformation and polarization on social media pose unprecedented challenges to the democratic process. New research from Aalto University and the University of Helsinki investigated how real-world shocks affect online discussions, using the Ukraine war and Finland’s NATO accession to understand how disinformation reinforces polarization.
‘The potential for democratic political participation in the world is greater than ever,’ says Tuomas Ylä-Anttila, associate professor of political science at the University of Helsinki. ‘At the same time, the deliberate use of disinformation by those who want to disturb democratic processes and generate polarization poses a threat to democracy and societal stability. This threat is now recognized widely, not just by political scientists but also organizations like the World Economic Forum.’
The research was a case study of how Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine affected discussions on NATO in the Finnish Twitter space immediately afterward. Finnish public opinion had long been split about joining NATO, with only around 20-30 percent in favour of joining the alliance. The Russian invasion led to a rapid convergence in favour of joining, which eventually led to Finland applying for membership. NATO and Russia are major themes in the campaigns for the Finnish presidential election, which will be held later this month.
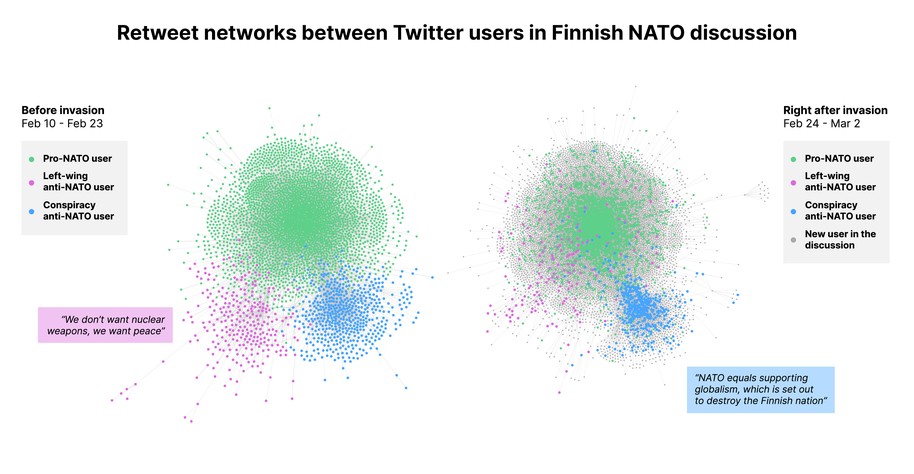
The Russian invasion quickly depolarized NATO discussions in Finland but was unable to break a social bubble built on disinformation and conspiracy theories. These findings hold lessons for how disinformation will affect political campaigns elsewhere in today’s rapidly changing world.
‘By analysing retweeting patterns, we found three separate user groups before the invasion: a pro-NATO group, a left-wing anti-NATO group, and a conspiracy-charged anti-NATO group,’ says Yan Xia, a doctoral researcher at Aalto and lead author of the study. ‘After the invasion, the left-wing anti-NATO group members broke out of their retweeting bubble and connected with the pro-NATO group despite their difference in partisanship, while the conspiracy-charged anti-NATO group mostly remained a separate cluster.’
The research revealed that the left-wing anti-NATO group and the pro-NATO group were bridged by a shared condemnation of Russia’s actions and shared democratic norms. The other anti-NATO group, mainly built around conspiracy theories and disinformation, consistently demonstrated a clear anti-NATO attitude.
‘An external threat can bridge partisan divides, but bubbles upheld by conspiracy theories and disinformation may persist even under dramatic external threats,’ says Ylä-Anttila.‘The continuity of these bubbles is likely explained by the notion that people within disinformation bubbles have limited communication with others outside their bubble, which tends to reinforce their prior beliefs.’
According to Ylä-Anttila, this effect is not limited to Finnish NATO discussions.
‘People who have strong, non-mainstream opinions are often more likely to hold on to their beliefs. They’re more prone to confirmation bias, meaning that they’re more likely to disregard information that is contrary to their own beliefs,’ says Ylä-Anttila.
‘For democratic decision-making, it’s essential to note that these disinformation bubbles are a part of our political reality and various actors that benefit from them – such as the Kremlin propaganda machine – will most likely try to exploit them.’
The research team consisted of network scientists from Aalto University and political scientists from the University of Helsinki. While network analysis can reveal the structure of user interactions and how it changes over time, analysing the content uncovers how the discussion climate evolves and what arguments connect or distinguish opposing sides. Combining research methods and expertise from computer science and social science offers a more holistic view of the discussions and dynamics on social media.
‘Network science methods enable us to measure structural polarization in these discussions and automate the search for different bubbles and other structures,’ says Mikko Kivelä, assistant professor at Aalto University. ‘In comparison to surveys, our methods are especially interesting because we can follow all of these discussions accurately after they have happened. In this research project, we were able to study and compare the discussions right before and right after the Russian invasion. We’re able to directly follow public discourse and the political elites that engage in it online.’
The research article was published in the European Physical Journal Data Science.
Research article: Xia, Y., Gronow, A., Malkamäki, A. et al. The Russian invasion of Ukraine selectively depolarized the Finnish NATO discussion on Twitter. EPJ Data Sci. 13, 1 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjds/s13688-023-00441-2
We are an internationally-oriented community and home to world-class research in modern computer science.

The number of Twitter bots and their influence on the Finnish municipal elections remained low. The final report of ELEBOT project provided new information especially on technical limitations in identifying bots.



