Coating bubbles with protein results in a highly stable contrast agent for medical use
Bacteria produce gas vesicles, tiny thin-walled sacs filled with air or fluid, to help them float. This phenomenon has captured the attention of scientists who see potential for similar bubble-based designs in fields like medicine. A team of researchers at Aalto University’s Department of Applied Physics, led by Professor Robin Ras, have now used the same idea to create a new kind of contrast agent for use in medical applications such as ultrasound imaging. The research was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Natural materials and biological inspiration
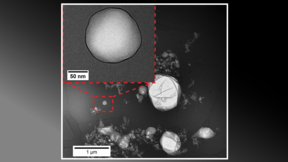
The researchers created bubbles, referred to as giant gas vesicles, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers in length, and measured their mechanical properties with a technique called micropipette aspiration. The bubbles were coated with proteins called hydrophobins, which come from fungi. In addition, the team developed a theory to better understand the intricacies of compressibility and porosity in micro-scale physics.
‘By studying the mechanical properties of gas vesicles and developing our own micropipette technique, we were able to make the bubbles stable enough to withstand pressures like the ones you would find in the human body. The bubbles function as a contrast agent, and potentially could be used to diagnose things like cardiological issues, blood flow, and liver lesions with ultrasound in the future,’ says Doctoral Researcher Hedar Al-Terke.
‘We have significantly extended the theoretical framework of the pipette aspiration technique. It can now be used to fully characterize the mechanical properties, including porosity, of compressible gas-filled systems such as the hydrophobin-coated bubbles used in this study,’ says Research Fellow Grégory Beaune.
The research on giant gas vesicles is part of the team’s focus on researching the medical applications of micro-scale physics.
More information:


OtaNano
OtaNano is Finland's national research infrastructure for micro-, nano-, and quantum technologies

Read more news

PORT_2026 brings Aalto students together to tackle culture, media, and climate challenges
Nearly 60 Aalto students joined the PORT_2026 Innovation Challenge, developing and pitching solutions addressing culture, media, and climate challenges.
Catalysis in a new light: Microscale interactions could enhance clean energy technologies
A new study provides a more detailed view of how catalysts function during chemical reactions. The discovery could help develop more efficient materials for applications such as green hydrogen production and a more sustainable chemical industry.
Physics Days 2026 gathered Finnish physicists to Aalto
The 2026 edition of the annual conference featured talks on moiré matter, women in physics and paper cuts.






