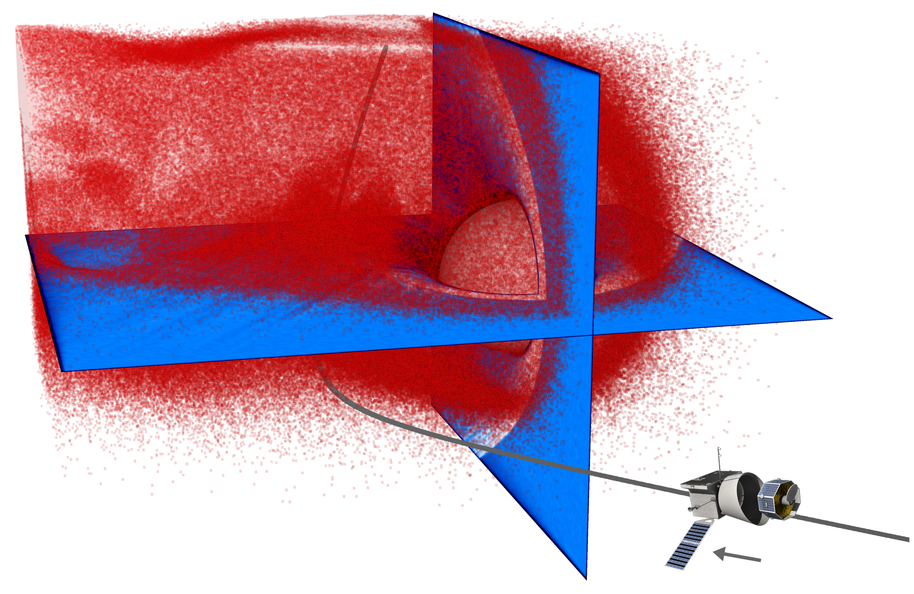
BepiColombo, en route to Mercury, flew by Venus – simulation shows clouds of particles escaping from the planet
The colour of the cloud leaving Venus indicates the density of the escaping particles: the redder the colour, the more escaping particles there are in the area. Simulation: Esa Kallio / Aalto Virtual Planetarium
The BepiColombo probe, a project of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), was launched on its journey to Mercury in October 2018. Although the journey will take approximately five more years, the first significant interim destination was reached already this week.
‘The BepiColombo probe made its first fly-by on 15 October at 6.58 Finnish time’, says Esa Kallio, professor at the Department of Electronics and Nanoeng at Aalto University. He has worked for 20 years at the SERENA instrument group that measures particles escaping from the atmospheres of planets.
‘The primary aim is to measure the particles from Mercury, but as we need to bypass Venus while we are on the way, we have the chance to test how the instruments work already now. Therefore, we can compare the space weather of both planets while on the same journey, which is a wonderful opportunity’, Kallio says.
Together with his colleagues, Esa Kallio has also developed a virtual space simulation in which the user can move in space and admire the different planets, including Venus.
‘In the Venus fly-by we can see a cloud of particles escaping from its atmosphere. One of the goals of our research is to understand the atmospheres of the different planets and their development – and in so doing, to learn about the atmosphere of our own Planet Earth. Venus and the Earth are neighbour planets, and they are often compared with each other. Venus is the hottest of the planets: a real inferno. There is approximately the same amount of carbon dioxide there as there is on Earth, but instead of the soil, almost all of it is in the atmosphere – and that is a situation that we do not want to have on Earth.’
Aalto University Research Fellow Riku Järvinen is part of the probe's Finnish-led SIXS instrument group, which measures high-energy solar particles and x-rays. The measurements help researchers in determining how elements are distributed on Mercury.
BepiColombo comprises two separate probes which will go into separate orbits after reaching Mercury. The probe has a total of 17 research instruments.
Would you like to fly past Venus on your own home sofa? You can download the Aalto Virtual Planetarium app from the address https://space.aalto.fi/software/ (VR glasses are needed).
Further information:
Professor Esa Kallio
tel. +358 50 420 5857
esa.kallio@aalto.fi
Research Fellow Riku Järvinen
tel. +358 50 357 4779
riku.jarvinen@aalto.fi
Read more news

The proxy server for remote access to e-resources is changing
If you have problems using e-resources, try accessing the e-resource using VPN connection.
A sustainable city is also age-friendly
Cities must involve older adults more strongly in the planning of the urban environment.
Renate Zhang’s journey in optimising the cost of creation
During the research program at Aalto University, Renate Zhang developed a cost-saving method that inspired her to pursue a doctoral degree.






