AI learns to type on a phone like humans
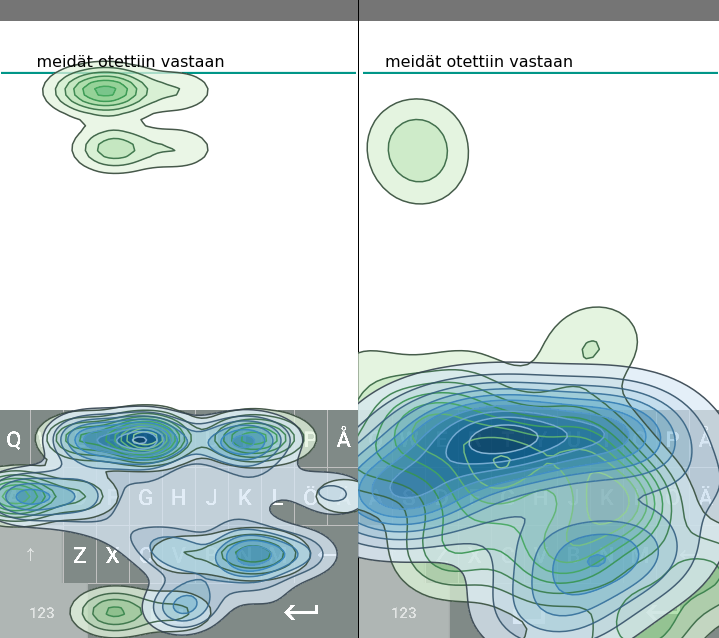
Touchscreens are notoriously difficult to type on. Since we can’t feel the keys, we rely on the sense of sight to move our fingers to the right places and check for errors, a combination of efforts we can’t pull off at the same time. To really understand how people type on touchscreens, researchers at Aalto University and the Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence FCAI have created the first artificial intelligence model that predicts how people move their eyes and fingers while typing.
The AI model can simulate how a human user would type any sentence on any keyboard design. It makes errors, detects them — though not always immediately — and corrects them, very much like humans would. The simulation also predicts how people adapt to alternating circumstances, like how their writing style changes when they start using a new auto-correction system or keyboard design.
‘Previously, touchscreen typing has been understood mainly from the perspective of how our fingers move. AI-based methods have helped shed new light on these movements: what we’ve discovered is the importance of deciding when and where to look. Now, we can make much better predictions on how people type on their phones or tablets,’ says Dr. Jussi Jokinen, who led the work.
The study, to be presented at ACM CHI on 12 May, lays the groundwork for developing, for instance, better and even personalized text entry solutions.
‘Now that we have a realistic simulation of how humans type on touchscreens, it should be a lot easier to optimize keyboard designs for better typing — meaning less errors, faster typing, and, most importantly for me, less frustration,’ Jokinen explains.
In addition to predicting how a generic person would type, the model is also able to account for different types of users, like those with motor impairments, and could be used to develop typing aids or interfaces designed with these groups in mind. For those facing no particular challenges, it can deduce from personal writing styles — by noting, for instance, the mistakes that repeatedly occur in texts and emails — what kind of a keyboard, or auto-correction system, would best serve a user.
Based on a method that teaches robots problem-solving
The novel approach builds on the group’s earlier empirical research, which provided the basis for a cognitive model of how humans type. The researchers then produced the generative model capable of typing independently. The work was done as part of a larger project on Interactive AI at the Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence.
The results are underpinned by a classic machine learning method, reinforcement learning, that the researchers extended to simulate people. Reinforcement learning is normally used to teach robots to solve tasks by trial and error; the team found a new way to use this method to generate behavior that closely matches that of humans — mistakes, corrections and all.
‘We gave the model the same abilities and bounds that we, as humans, have. When we asked it to type efficiently, it figured out how to best use these abilities. The end result is very similar to how humans type, without having to teach the model with human data,’ Jokinen says.
Comparison to data of human typing confirmed that the model's predictions were accurate. In the future, the team hopes to simulate slow and fast typing techniques to, for example, design useful learning modules for people who want to improve their typing.
The paper, Touchscreen Typing As Optimal Supervisory Control, will be presented 12 May 2021 at the ACM CHI conference.
More media
- Download videos of AI typing, including making and correcting errors, and visualisation from Aalto Material Bank: https://materialbank.aalto.fi/l/N5sQmD5qpD69
- The researchers made me type this
- I make typos so you don’t have to
- Look ma no hands
- Find the paper and other materials: https://userinterfaces.aalto.fi/touchscreen-typing/
Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence
The Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence FCAI is a research hub initiated by Aalto University, the University of Helsinki, and the Technical Research Centre of Finland VTT. The goal of FCAI is to develop new types of artificial intelligence that can work with humans in complex environments, and help modernize Finnish industry. FCAI is one of the national flagships of the Academy of Finland.

Read more news

Apply Now: Unite! Visiting Professorships at TU Graz
TU Graz, Austria, invites experienced postdoctoral researchers to apply for two fully funded visiting professorships. The deadline for expressions of interest is 20 February 2026, and the positions will begin on 1 October 2026.
Hanaholmen’s 50th anniversary exhibition lives on online – making the history of Finnish–Swedish cooperation accessible worldwide
MeMo Institute at Aalto University has produced a virtual 3D version of the anniversary exhibition of Hanaholmen.
Environmental Structure of the Year 2025 Award goes to Kalasatama-Pasila tramway
The award is given in recognition of meritorious design and implementation of the built environment. Experts from Aalto University developed sustainability solutions for the project.






