Toward a team that is able to achieve its potential
Information asymmetry is the starting point in diverse teams
To solve ill-defined problems, we assemble teams (a group of people who come together to achieve a common goal) made up of members who possess a wide range of knowledge, expertise, and understanding related to the challenge at hand. This kind of situation means that the starting point is information asymmetry, with team members holding distinct, unshared information. However, it is easy for such a team to focus instead on discussing information that is commonly held. The usual reasons for this are that:
- It is easier to discuss issues widely known, and it takes courage to bring new points of view to the table
- Team members may falsely assume that certain knowledge is commonly known and are unaware that others lack some of the knowledge they have
- Team members may fear to expose their ignorance in front of experts from different disciplines, which may lead to a situation where “stupid” questions are never asked, and privately held information is never shared.
If the team is unable to create circumstances where individually held information and knowledge is shared, team performance begins to suffer. This highlights the dual responsibilities of people working in a diverse team: They must be willing and able to actively share their points of view with others while at the same time be curious about the ideas and thoughts of others, and actively listen to them.
Inviting others to join the discussion to create a shared understanding
No matter how effective a team might be in managing its activities and resources, if it is unable to create circumstances where frequent communication and respectful interaction happen, it will fail to achieve its potential as well as the best possible solution.
When we approach ill-defined problems where there rarely is only a single possible solution, the team must be able to take action despite the discomfort of uncertainty and ambiguity that are present in various forms. The key lies in finding links between the different perspectives and inviting others into the discussion to create shared understanding. Respectful interaction that fosters frequent and open communication is built through small steps such as positive reactions, words of encouragement, and intuiting how others feel.
Unlocking the potential of a diverse team
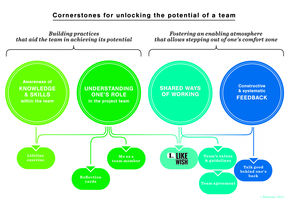
For a diverse team to successfully harness its potential to solve ill-defined problems, it must create practices that help the team achieve that potential and, concurrently, create an atmosphere that allows team members to step outside their comfort zones. The following four practices build the foundation for teamwork:
-
Awareness of the skills and knowledge within the team
The better and sooner that team members understand each other’s skills, experiences, and capabilities, the easier it is to utilise those throughout the project. When solving ill-defined problems, we must see beyond our educational backgrounds, because the valuable insight into the challenge at hand may come from another type of understanding.
-
Understanding one’s role on the project team
Role-related uncertainty and ambiguity may impede team members from fully utilising their knowledge in a project. Unless team members recognise their inputs as necessary and valuable, they may tend to hold back or believe their contribution is irrelevant.
-
Shared ways of working
Practices that are built early on tend to stick throughout a project and create a structure for solutions. However, these mutually agreed-upon practices must be cultivated along the way.
-
Constructive and systematic feedback
The feedback that is provided systematically and safely supports open communication and builds an atmosphere of trust. It also has the power to eliminate assumptions of ourselves and those of others.
Teamwork First-Aid Kit: Tools to support teamwork in project courses
Teamwork First-Aid Kit gathers tools that have proved to be useful in supporting diverse teams tackling ill-defined problems and building foundational elements for the successful teamwork strategies presented above. It is a small step toward educating game-changers who can make the team more than a sum of its parts. Undeniably, teamwork skills are among the most pivotal work-life skills that younger generation entering the workforce are expected to master.
Teamwork First-Aid Kit is a Teaching Lab / Learning Challenge Aalto Pilot and was supported by the Pilot Funding. Visual identity and graphic design of the toolkit has been created by Anna Kuukka, Aalto Design Factory & School of Engineering.
Author:

Satu Rekonen is a postdoctoral researcher at Aalto University School of Science whose mission is to educate game-changers who can support a team in achieving its potential. Satu is passionate about improving understanding of how diverse teams approach ill-defined problems and the struggles they face while doing so.
Read more news

9 experts on Finnish happiness: From cold-water swimming to trust in institutions, why does the nation stay happy?
The latest research from Aalto offers a variety of possible explanations.
What motherhood reveals about modern work
Workplace norms still demand that the realities of motherhood are hidden, but organisations must accept that careers now unfold differently, says Professor Taija Turunen.
Professor of Finance Petri Jylhä is Teacher of the Year 2026
Every autumn, students at the School of Business vote for the best teacher, who is then honoured at the KY Annual Ball






