Stopping the unstoppable with atomic bricks
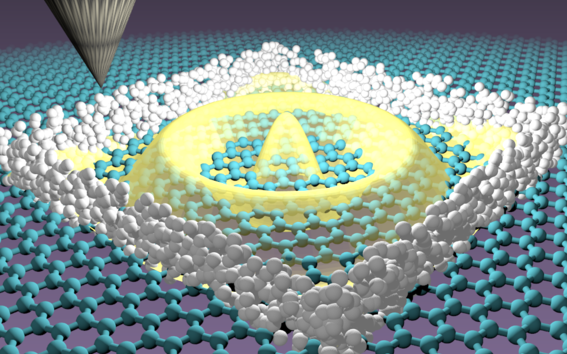
Graphene's unique 2D structure means that electrons travel through it differently to most other materials. One consequence of this unique transport is that applying a voltage to them doesn't stop the electrons like it does in most other materials. This is a problem because to make useful applications out of graphene and its unique electrons like quantum computers, it is necessary to be able to stop and control graphene electrons.
An interdisciplinary team of scientists from the Universidad Autonoma de Madrid (Spain), Université Grenoble Alpes (France), International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory (Portugal) and Aalto University has managed to solve this long-standing problem. They combined experimental researchers including Eva Cortés del Río, Pierre Mallet, Héctor González‐Herrero, José María Gómez‐Rodríguez, Jean‐Yves Veuillen and Iván Brihuega with theorists, including Joaquín Fernández-Rossier and Jose Lado, assistant Professor in the department of Applied Physics at Aalto.
The experimental team used atomic bricks to build walls capable of stopping the graphene electrons. This was achieved by creating atomic walls that confined the electrons, leading to structures whose spectrum was then compared with theoretical predictions, demonstrating that electrons were confined. In particular, it was obtained that the engineered structures gave rise to nearly perfect confinement of electrons, as demonstrated from the emergence of sharp quantum well resonances with a remarkably long lifetime.
The work, published this week in Advanced Materials, demonstrates that impenetrable walls for graphene electrons can be created by collective manipulation of a large number of hydrogen atoms. In the experiments, a scanning tunnelling microscope was used to construct artificial walls with sub nanometric precision. This led to graphene nanostructures of arbitrarily complex shapes, with dimensions ranging from two nanometres to one micron.
Importantly, the developed method is non-destructive, allowing to erase and rebuild the nanostructures at will, providing an unprecedented degree of control to create artificial graphene devices. The experiments demonstrate that the engineered nanostructures are capable of perfectly confining the graphene electrons in these artificially designed structures, overcoming the critical challenge imposed by Klein tunnelling. Ultimately, this opens up a plethora of exciting new possibilities, as the created nanostructures realize graphene quantum dots that can be selectively coupled, opening ground-breaking possibilities for artificially designed quantum matter.
Read More
“Quantum Confinement of Dirac Quasiparticles in Graphene Patterned with Sub‐Nanometer Precision” Advanced Materials https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202001119
Contact

Read more news
Soil Laboratory Exhibition – Exploring the Dialogue Between Human and the Earth in Utsjoki
Soil Laboratory explores the relationship between humans and the earth as a living landscape through ceramic practices in Utsjoki.
The Finnish Cultural Foundation awarded grants for science and art
A total of 15 individuals or groups from Aalto University received grants
Environmental Structure of the Year 2025 Award goes to Kalasatama-Pasila tramway
The award is given in recognition of meritorious design and implementation of the built environment. Experts from Aalto University developed sustainability solutions for the project.






