New textiles developed at Aalto University change shape when they heat up, giving designers a wide range of new options. In addition to offering adjustable aesthetics, responsive smart fabrics could also help monitor people’s health, improve thermal insulation, and provide new tools for managing room acoustics and interior design.
The new fabrics weave together old technology and a new approach. Liquid crystalline elastomers (LCEs) were developed in the 1980s. LCEs are a smart material that can respond to heat, light, or other stimuli, and they’ve been used as thin films in soft robotics. Although LCEs have been made into fibres, so far they haven’t been made into textiles.
In collaboration with researchers at the University of Cambridge, a team from the Multifunctional Materials Design research group at Aalto, led by Prof. Jaana Vapaavuori, has now used LCE yarns to make woven fabric using conventional textile crafting techniques and tested how they behave.

The team wove LCE yarn in different patterns to make plain fabric, satin, twill, and a weft rib fabric. They made two versions of each pattern using either a soft or stiff LCE yarn, and then they tested how the different fabrics responded to heat from an infrared lamp.
All of the LCE fabrics contracted as they warmed up, though the exact response differed from pattern to pattern. The changes were reversible – the patterns relaxed back to their original shape as their temperature dropped.
‘At first, the impact of using industrial textile techniques with these kinds of new materials wasn’t clear to us. The elasticity of the two types of LCE yarn is comparable to spandex or even softer. That meant it was essential to understand if the textile industry could use these yarns and how the combination with conventional yarns would impact their movement,’ says Pedro Silva, a postdoctoral researcher at Aalto who led the study.
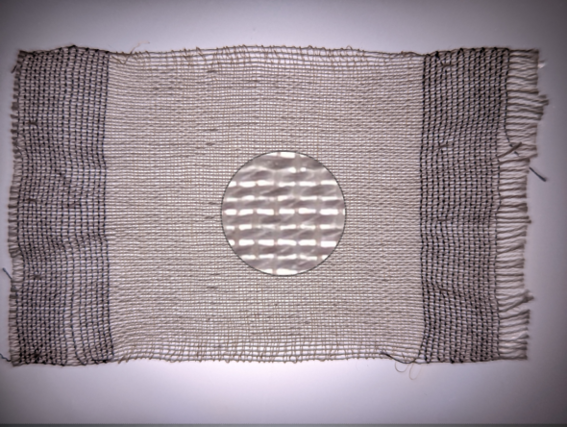

Next, the team combined LCE yarns with linen and nylon in a radial pattern to weave a circle that would lift itself into a cone when heated. Heating the pattern caused the LCE yarn to contract, pulling the cloth up into a cone. As it cooled, the cone relaxed back into a flat circle.
This proof-of-concept brings smart, reactive textiles one step closer to reality. ‘From day one of this project, we took on the challenge of working with experts spanning different disciplines at two institutes. The research succeeded and benefited tremendously from this multidisciplinarity, and now the results are openly available. We hope our work will trigger new ways of thinking when it comes to the materials of tomorrow,’ says Maija Vaara, an AaltoPhD student who crafted the weaves and laces.
The findings were published in Advanced Materials.

Read more news

VTT, Aalto University and GTK: How to ensure Finland captures the multi‑billion growth potential of mineral economy
Finland is rising to the forefront of the mineral economy through new research initiatives and closer collaboration
Significant donation to boost pavement engineering research and education
Companies and associations in the field have donated €400,000 to the School of Engineering.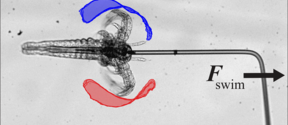
‘Mesoscale’ swimmers could pave way for drug delivery robots inside the body
Researchers have discovered how tiny organisms break the laws of physics to swim faster — such secrets of mesoscale physics and fluid dynamics can offer entirely new pathways for engineering and medicine.






