Researchers create the most water-repellent surface ever
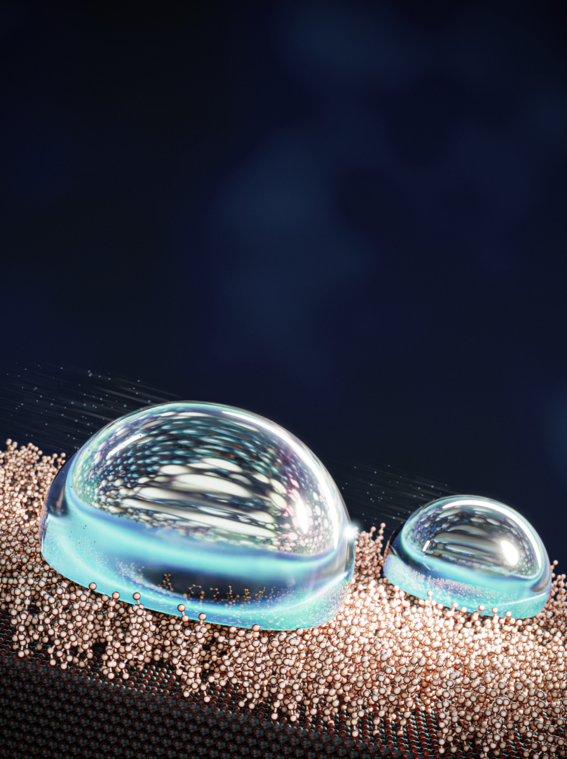
Researchers have developed a new mechanism to make water droplets slip off surfaces, described in a paper published in Nature Chemistry. The discovery challenges existing ideas about friction between solid surfaces and water and opens up a new avenue for studying droplet slipperiness at the molecular level. The new technique has applications in a range of fields, including plumbing, optics, and the auto and maritime industries.
All around us, water is always interacting with solid surfaces. Cooking, transportation, optics and hundreds of other applications are affected by how water sticks to surfaces or slides off them. Understanding the molecular dynamics of these microscopic droplets helps scientists and engineers find ways to improve many household and industrial technologies.
Liquid-like surfaces are a new type of droplet-repellent surface that offer many technical benefits over traditional approaches—a topic recently reviewed in Nature Reviews Chemistry by Aalto University Professor Robin Ras. They have molecular layers that are highly mobile yet covalently tethered to the substrates, giving solid surfaces a liquid-like quality acting like a layer of lubricant between the water droplets and the surface itself. A research team led by Ras used a specially-designed reactor to create a liquid-like layer of molecules, called self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), on top of a silicon surface.
Watching self-assembled monolayers grow
‘Our work is the first time that anyone has gone directly to the nanometer-level to create molecularly heterogenous surfaces,’ says doctoral researcher Sakari Lepikko, lead author of the study.
By carefully adjusting conditions such as temperature and water content inside the reactor, the team could fine-tune how much of the silicon surface the monolayer covered.
“I find it very exciting that by integrating the reactor with an ellipsometer, that we can watch the self-assembled monolayers grow with extraordinary level of detail,” says Ras.
‘The results showed more slipperiness when SAM coverage was low or high, which are also the situations when the surface is most homogeneous. At low coverage, the silicon surface is the most prevalent component, and at high, SAMs are the most prevalent.’
‘It was counterintuitive that even low coverage yielded exceptional slipperiness,’ Lepikko continues.
At low coverage, the water becomes a film over the surface, which had been thought to increase the amount of friction. ‘We found that, instead, water flows freely between the molecules of the SAM at low SAM coverage, sliding off the surface. And when the SAM coverage is high, the water stays on top of the SAM and slides off just as easily. It’s only in between these two states that water adheres to the SAMs and sticks to the surface.”
The new method proved exceptionally effective, as the team created the slipperiest liquid surface in the world.
Anti-fogging, de-icing, self-cleaning
The discovery promises to have implications wherever droplet-repellent surfaces are needed. According to Lepikko, this covers hundreds of examples from daily life to industrial solutions.
‘Things like heat transfer in pipes, de-icing and anti-fogging are potential uses. It will also help with microfluidics, where tiny droplets need to be moved around smoothly, and with creating self-cleaning surfaces. Our counterintuitive mechanism is a new way to increase droplet mobility anywhere it’s needed,’ Lepikko says.
Next, the team plans to continue experimenting with their self-assembling monolayer setup and improve the layer itself. Lepikko is particularly excited about the information this work has provided for future innovations.
‘The main issue with a SAM coating is that it’s very thin, and so it disperses easily after physical contact. But studying them gives us fundamental scientific knowledge which we can use to create durable practical applications.’
The research used the national research infrastructure OtaNano was carried out by the Soft Matter and Wetting group at the Department of Applied Physics, which has also produced other pioneering water-repellent materials.
Researchers from the University of Jyväskylä also contributed to this study.
Ras also published this year in Nature Reviews Chemistry a deep-dive into omniphobic liquid-like surfaces (LLS) and their promising utility. These LLSs could enable novel applications due to their ability to control slip, friction and adhesion properties.

Read more news

Apply Now: Unite! Visiting Professorships at TU Graz
TU Graz, Austria, invites experienced postdoctoral researchers to apply for two fully funded visiting professorships. The deadline for expressions of interest is 20 February 2026, and the positions will begin on 1 October 2026.
Hanaholmen’s 50th anniversary exhibition lives on online – making the history of Finnish–Swedish cooperation accessible worldwide
MeMo Institute at Aalto University has produced a virtual 3D version of the anniversary exhibition of Hanaholmen.






