Designer materials with completely random structures might enable quantum computing
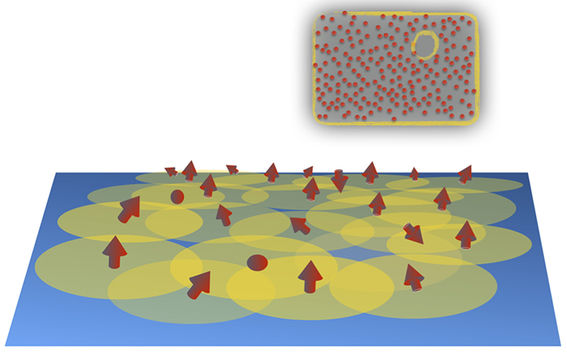
Randomly sprinkled magnetic atoms (red arrows) on a superconducting surface may give rise to a topological superconducting phase. Inset: The onset of the topological phase is signalled by the appearance of so-called Majorana edge mode encircling the system. Image: Teemu Ojanen.
Designing quantum materials with exotic and unprecedented electrical properties has the field of physics teeming with buzz. Researchers at Aalto University in Finland have now introduced a significant turn in this discussion by developing an amorphous material which exhibits topological superconductivity. Until this point, these materials have required highly regular structures to show desired electrical properties.
The findings, published in Nature Communications, bring the field one step closer to application. Topological superconductors and insulators are considered to be possible building blocks of lossless components for quantum computers. While topological superconductors might not exist in nature, they can be fabricated, as the study demonstrates.
‘We have presented a method of fabricating topological materials in amorphous systems with randomly placed constituents. This means we can achieve superconductivity in the material by sprinkling magnetic atoms on a superconducting surface completely at random, not in highly-defined and ornamented lattices, for example,’ explains doctoral student Kim Pöyhönen.
The recent boom on topological superconductors stems mainly from an unconventional quantum-level phenomenon, a collective movement of many individual particles called Majorana fermion excitations. They have been envisioned as critical ingredients of topological quantum computers.
‘Getting highly irregular, random systems to work as topological superconductors will potentially make their fabrication and manufacture much more convenient compared to current methods,’ says research group leader, Docent Teemu Ojanen.
Perhaps for now, the implications of the random quantum material verge only on fundamental research, but that might not be the case for much longer.
‘For topological quantum matter to find its way to actual applications, it’s imperative we find even more new candidates for amorphous topological materials,’ states Ojanen.
Further information:
Teemu Ojanen, Docent
Theory of Quantum Matter group
Department of Applied Physics
Aalto University
teemu.ojanen@aalto.fi
tel. +358 40 510 5406
Read more news

Applications open for Innovation Postdoc in AI
A fully funded, 12–18 month career track to turn your doctoral discoveries into deep-tech startups.
VTT, Aalto University and GTK: How to ensure Finland captures the multi‑billion growth potential of mineral economy
Finland is rising to the forefront of the mineral economy through new research initiatives and closer collaboration
Significant donation to boost pavement engineering research and education
Companies and associations in the field have donated €400,000 to the School of Engineering.