CEST researchers pave the way for calculating circular dichroism (CD) spectra more efficiently
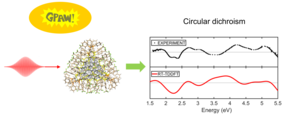

Members of the CEST group published a recent paper introducing a novel method to calculate CD spectra in the open source GPAW code. The publication shows that the implemented approach is more efficient than the commonly used linear-response method and can easily calculate CD spectra of nanoscale systems, such as hybrid silver clusters composed of over 1000 atoms.
Recording CD spectra is a very powerful method to study the chiral optical properties and detect small structure changes in chiral molecules, DNA, proteins and nanoclusters, to name a few. However, the computational cost of commonly used linear-response time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) methodology increases drastically with the system size under observation, and can typically only be applied to small systems. To overcome this challenge, researchers Esko Makkonen, Tuomas Rossi, Patrick Rinke and Xi Chen worked with collaborators from Jyväskylä, Spain and Colombia to implement a more efficient approach based on real-time TDDFT to calculate CD spectra. The published code offers both linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) and grid modes. The LCAO mode is beneficial for large systems, while the grid mode is suitable for small molecules and benchmark purposes, thus making this new method extremely versatile.
The authors tested this new implementation on various systems. In all test cases, the calculations show high efficiency and agree well with experimental results and reference computations. Driven by this initial success, the group is now ready to study many more chiral nanoclusters. The aim of this work is to discover the origin of chiral optical properties in nanoclusters, and design metal clusters which are useful as chiral sensors.
This paper is published in The Journal of Chemical Physics. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0038904
Read more news

Aalto University is introducing ORCID’s Researcher Connect service
Aalto University is introducing ORCID's Researcher Connect service, which facilitates information transfer between researchers' ORCID profiles and the university's research information management system, ACRIS.
Nature of Process: Exhibition by the students of the ‘Personal Exploration’ Course
Nature of Process is a multi-material exhibition of 14 Master´s students of Aalto ARTS
Doc+ connects research impact with career direction - join the events!
Doc+ panels have brought together wide audiences in February and continue in March with two events to discuss doctoral careers and their diversity.






