Auroral crackling sounds are related to the electromagnetic resonances of the Earth
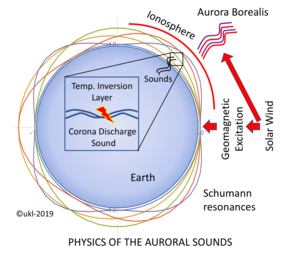
The study is a continuation of a hypothesis that Unto K. Laine, Professor Emeritus, published three years ago on the origin of the sounds heard during the displays of the Northern Lights. His theory postulated that the sounds are generated when a magnetic storm causes charges in the temperature inversion layer of the lower atmosphere, to be discharged at an altitude of 70 to 80 metres.
A recent research paper presented by Laine at the ICSV26 congress in Montreal provides a more detailed account of the sound generation. According to this study, when the Northern Lights occur, the spectrum of the temporal envelope of the crackling noise (or in other words, the rapid changes in the sound amplitude) contain frequencies of the Schumann resonances.
The Schumann resonances refer to the low-frequency electromagnetic resonances occurring around the Earth, the strongest of them being below 50 Hz. Laine has now observed that these resonances generated similar rhythmic structures in all the measured crackling sounds.
’Previous international research has shown that a geomagnetic storm occurring during the Northern Lights reinforces the Schumann resonances. For the first time, such resonances have been found to activate the sound generation mechanism in the temperature inversion layer at altitudes of between 70 to 80 metres where the accumulated electric charges give rise to corona discharges and crackling sounds. In addition to the nine lowest Schumann resonances, the spectra also include their difference and sum frequencies or in other words, distortion components. This non-linearity also lends support to the hypothesis of auroral sounds generation,’ Laine says.
The research material consisted of 25 sound events measured on the ground in September 2001 and in March 2012 in Southern Finland, during the display of active Northern Lights. Although the measurements were conducted at different locations using various equipment, the results nevertheless point to the same direction.
The results will be published today (10 July) at the ICSV26 congress in Montreal, which brings together more than 2,000 researchers in acoustics from around the globe.
Further information:
Unto K. Laine, Professor Emeritus
Read more news

Demo Day breaks records in 2026: Inside Otaniemi’s fastest growing startup showcase
Hosted by Aalto Startup Center and A Grid, Demo Day brought together nearly 800 visitors, 90 startup booths, and over 75 investors. What began as a grassroots gathering in 2018 has grown into one of Finland’s most vibrant startup showcases.
Catalysis in a new light: Microscale interactions could enhance clean energy technologies
A new study provides a more detailed view of how catalysts function during chemical reactions. The discovery could help develop more efficient materials for applications such as green hydrogen production and a more sustainable chemical industry.The campus welcomes its third Learning Lounge
Learning Lounge makes a new expansion into Restaurant Aalto Kvarkki on 16 March.






