A unique set of observations revealed: Solar radio brightenings behave like a beating heart
The Sun has been studied at Aalto University's Metsähovi Radio Observatory for 40 years. To study our closest star, researchers use a unique technique, which allows them to make observations at several locations around the world simultaneously. The Sun gives us life, but it can also interfere with our lives, as many systems that are important to modern society are disrupted when a solar storm hits. The problems caused by a potential solar storm are so serious that solar storms have been included in the Ministry of the Interior’s National Risk Assessment as one of the risks that threaten us.
Predicting solar storms is difficult because the phenomenon involves many variables. The Sun's activity has an eleven-year cycle, which makes it possible to estimate when the Sun is at its most active. The direction of a solar storm is also important. Only a storm that is directly facing the earth would be devastating but even the researchers cannot predict the extent of the destruction.
‘We can only speculate what it would mean, for example, for satellites and wireless communications. In 2015, a very strong solar storm disrupted the Swedish air traffic radar so that air traffic had to be suspended for a while, ‘says Juha Kallunki, Laboratory Engineer responsible for solar observations at Metsähovi.
The amount of observational data available has rocketed
The Sun can be studied in many ways. Some researchers focus on examining individual short-term changes, and some are investigating the Sun's behaviour based on long time observations. The amount of observational data has increased exponentially in recent decades as research equipment has developed. In order to achieve a better resolution, the Sun can now be observed simultaneously by several radio telescopes rather than one. This makes it possible to examine even the Sun’s smallest structures. Researchers are also able to analyse more accurately the rapid physical phenomena occurring in the Sun.
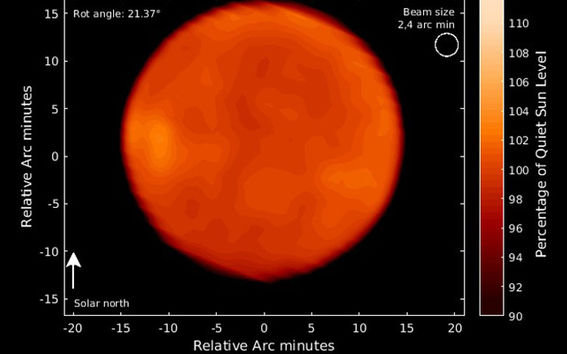
Sunspots have been studied with telescopes for hundreds of years. Solar radio maps produced by Metsähovis’s 14-meter radio telescope have shown that sunspots visible to the naked eye do not tell the whole truth about the Sun’s activity. Particularly when the Sun is active, solar radio brightenings appear as warm areas on the solar radio maps. They can often be seen in the same place as sunspots. Based on the radio observations made at Metsähovi, it has been detected that solar radio brightenings are pulsating at regular intervals. The Sun is pumping hot plasma from deep within into the solar radio brightenings at intervals ranging from few minutes to an hour.
The first solar radio maps were observed at Metsähovi in September 1978. During the summer time, due to our northern location it is possible to do even 16-hour continuous solar observations. Observations on the radio area can also be made on a cloudy day.
Inquiries:
Juha Kallunki
Laboratory Engineer
Metsähovi Radio Observatory, Aalto University
email: juha.kallunki@aalto.fi
tel: 029-4424852
Read more news
‘Mesoscale’ swimmers could pave way for drug delivery robots inside the body
Researchers have discovered how tiny organisms break the laws of physics to swim faster — such secrets of mesoscale physics and fluid dynamics can offer entirely new pathways for engineering and medicine.
Hanaholmen’s 50th anniversary exhibition lives on online – making the history of Finnish–Swedish cooperation accessible worldwide
MeMo Institute at Aalto University has produced a virtual 3D version of the anniversary exhibition of Hanaholmen.
Research reveals the economic significance of family firms in Finland
The findings show that, on average, family firms are more profitable and financially resilient than other firms – and also invest more.






