A surprising experiment opens the path to new particle manipulation methods
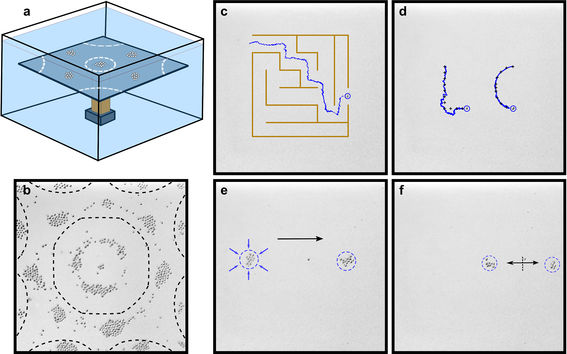
Researchers at Aalto University have discovered a surprising phenomenon that changes how we think about how sound can move particles. Their experiment is based on a famous experiment recognisable from high school science classrooms worldwide – the Chlandni Plate experiment, where particles move on a vibrating surface. The experiment was first performed in from 1787 by Ernst Chladni, who is now known as the father of acoustics. Chladni’s experiment showed that when a plate is vibrating at a frequency, heavy particles move towards the regions with less vibration, called nodal lines. This experiment has been extensively repeated during the centuries since, and shaped the common understanding of how heavy particles move on a vibrating plate. But researchers at Aalto University have now shown a case where heavy particles move towards the regions with more vibrations, or antinodes. “This is a surprising result, almost a contradiction to common beliefs,” says Professor Quan Zhou.
The researchers installed a silicon plate on a piezoelectric transducer and submerged it into water. They spread sub-mm glass spheres on the plate, and vibrated the plate with signals of different frequencies, creating waves on the plate. The researchers were then surprised to observe that the particles move towards the antinodes, forming what they have dubbed “inverse Chladni patterns”.
An interesting aspect is that the system can create predictable motion at a wide range of frequencies. “We can move particles at almost any frequency, and we do not rely on the resonance of the plate”, says Zhou. “This gives us a lot of freedom in motion control”.
Using the newly discovered phenomenon, the researchers were able to precisely control the motion of single particles and a swarm of particles on the submerged plate. In one example, they moved a particle in a maze on the plate, wrote words consisting of separate letters, and merged, transported and separated a swarm of particles by playing different musical notes.
“Many procedures in pharmaceutical research and microsystem assembly require the ability to move and manipulate small particles easily. Using just a single actuator to do all these different things, we are opening a path to new particle handling techniques”, says Zhou. “Additionally, the method can inspire the future factory-on-a-chip systems.”
Contact:
Professor Quan Zhou
quan.zhou@aalto.fi
Read more news
Soil Laboratory Exhibition – Exploring the Dialogue Between Human and the Earth in Utsjoki
Soil Laboratory explores the relationship between humans and the earth as a living landscape through ceramic practices in Utsjoki.
The Finnish Cultural Foundation awarded grants for science and art
A total of 15 individuals or groups from Aalto University received grants
Environmental Structure of the Year 2025 Award goes to Kalasatama-Pasila tramway
The award is given in recognition of meritorious design and implementation of the built environment. Experts from Aalto University developed sustainability solutions for the project.






