Novel cross-disciplinary approach for identifying complex molecular adsorbates
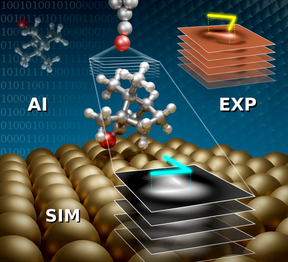

Hybrid functional materials combine organic and inorganic components and have many advantageous properties. They are commonly utilized in emerging technologies, such as novel electronic devices and green energy solutions. Controlling the properties of these materials requires detailed knowledge of their atomic structure, in particular the configuration of molecular adsorbates in the hybrid organic-inorganic interface. Identifying the structure of bulky non-planar adsorbates is often unattainable, even with current state-of-the-art tools. Interpreting the structure of bulky molecules from atomic force microscopy (AFM) images is challenging, and finding the stable structures using quantum mechanical simulations is computationally intractable with conventional methods. In a recent work by Jari Järvi, Benjamin Alldritt, Ondřej Krejčí, Milica Todorović, Peter Liljeroth and Patrick Rinke, a new cross-disciplinary method was developed to identify bulky adsorbates by combining artificial intelligence structure search with AFM simulations and experiments.
In this fresh approach, the stable model structures are first identified using the Bayesian Optimization Structure Search (BOSS) artificial intelligence tool, which was recently developed in CEST. The best candidate structures are scanned into stacks of images using AFM simulations with different heights of the microscope tip. The model structures are correlated to experiments by comparing image features in the stacks of simulated and experimental AFM images, which allows identifying the experimental configurations. In a recent article, J. Järvi et al. have demonstrated this method by identifying the structure of (1S)-camphor (a typical bulky molecule) on the Cu(111) surface. This material has been previously studied with AFM, but inferring the structure from the images has been inconclusive. Using this novel approach, they successfully identified three distinct configurations of (1S)-camphor on Cu(111) in the experiments.
The presented method can be applied to other adsorption structure search problems and combined with other experimental techniques. Analyzing single molecules is only the first step towards studying more complex molecular assemblies and subsequently the formation of monolayers. The acquired structural insight can help to optimize the functional properties of these materials.
The research article is published in Advanced Functional Materials and is now available online https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202010853.
Read more news
Soil Laboratory Exhibition – Exploring the Dialogue Between Human and the Earth in Utsjoki
Soil Laboratory explores the relationship between humans and the earth as a living landscape through ceramic practices in Utsjoki.
The Finnish Cultural Foundation awarded grants for science and art
A total of 15 individuals or groups from Aalto University received grants
Environmental Structure of the Year 2025 Award goes to Kalasatama-Pasila tramway
The award is given in recognition of meritorious design and implementation of the built environment. Experts from Aalto University developed sustainability solutions for the project.






